Test Your Ovarian Reserve to Determine Fertility Potential
Testing for ovarian reserve is a term used to describe some basic tests which are helpful in determining a woman’s fertility potential.
More specifically, circulating hormone levels are measured as useful markers of the efficiency of her ovaries and how likely she is to respond to IUI or IVF treatments.
The tests also provide an assessment of the health of the eggs at the time the testing is performed. In other words, the test results provide the odds of producing healthy eggs during a treatment cycle.
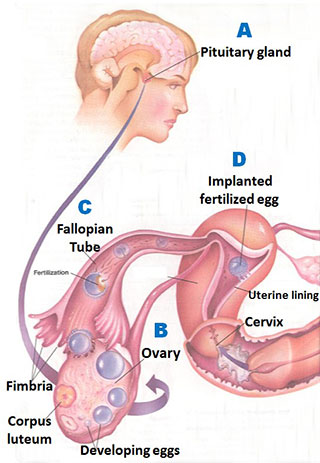
The image displays the intricate process of fertilization starting with the FSH and LH hormones in the pituitary gland.
How to Test Your Egg Quality
A blood sample is obtained between the 3rd through the 5th day of your menstrual cycle and it can provide useful information about your ovarian reserve. For your convenience, we offer this test at West Coast Fertility Centers located in Orange County, Southern California. Our ovarian reserve panel consists of the following blood hormone levels: FSH, LH, Estradiol, TSH and Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH). You can calculate the correct day to undergo this testing by documenting the first full day of menstrual bleeding and contacting our center to schedule your tests: 714-513-1399.
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone): A woman’s pituitary gland releases FSH hormone to the ovaries triggering follicle recruitment which leads to the selection of the dominant egg in that cycle. Fluid-filled sacs called follicles contain the egg and send a chemical signal to the pituitary gland causing the FSH level to taper off and remain in the lower favorable range. Less robust ovaries and follicles respond weakly and the FSH climbs higher into the unfavorable range.
How to Read Your FSH Level
| Range | Ovarian Function |
|---|---|
| 2 – 8 | Excellent |
| 8 – 10 | Good |
| 10 – 12 | Fair |
| > 12 | Guarded |
There can be some variation in FSH levels from month to month but generally speaking, high levels of FSH indicate that your ovarian reserve is low and egg quality may be diminished. In humans, there is a normal physiologic rise in FSH levels with increasing age which can signal lower pregnancy rates.
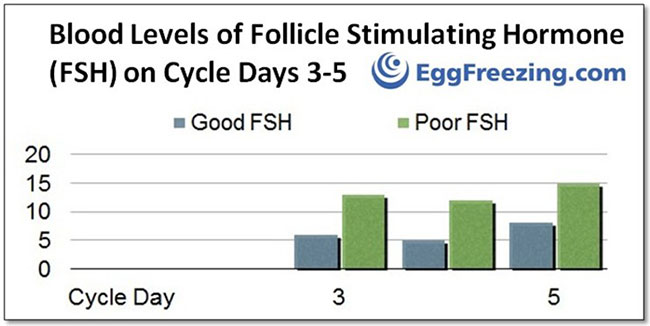
The graph above shows that blood levels of FSH on cycle days 3 through 5 can suggest reassuring or non-reassuring ovarian reserve.
When FSH is elevated, it is useful to measure this hormone one or more times to document the trend in a woman’s level.
Additional Ovarian Reserve Testing
During the first several days of the menstrual cycle, it is possible to count the number of resting follicles in each ovary (AFC) and therefore utilized as an additional tool in helping select the best treatment for our patients. This test is performed painlessly and quickly by an ultrasound scan. The test can be performed in 10 minutes and results are available immediately.
For more information about how to test your ovarian reserve, please contact our egg freezing patient coordinator at 714-513-1399.